Save / Exit / Edit Vim
How to Save a File in Vim / Vi and Quit the Editor
Vim is the text editor of choice for many users that spend a lot of time on the command line. Unlike other editors, Vim has several modes of operation, which can be a little intimidating for new users.
Vim or its precursor Vi comes preinstalled on macOS and almost all Linux distributions. Knowing the basics of Vim will help you when you encounter a situation where your favorite editor is not available.
This guide explains how to save a file in Vim / Vi and quit the editor.
Vim Modes
When you launch the Vim editor, you’re in normal mode. In this mode, you can use vim commands and navigate through the file.
To type a text, you need to enter the insert mode by pressing the i key. This mode allows you to insert and delete characters in the same way you do in a regular text editor .
To go back to the normal mode from any other mode, just press the Esc key.
Open a File in Vim / Vi
To open a file using Vim, launch your terminal and type vim followed by the name of the file you want to edit or create:
vim file.text
Another way to open a file is to start the editor and type :e file_name, where file_name is the name of the file you want to open.
Save a File in Vim / Vi
The command to save a file in Vim is :w.
To save the file without exiting the editor, switch back to normal mode by pressing Esc, type :w and hit Enter.

- Press
Esc - Type
:w - Press
Enter
There is also an update command :up, which writes the buffer to the file only if there are unsaved changes.
To save the file under a different name, type :w new_filename and hit Enter.
Save a File and Quit Vim / Vi
The command to save a file in Vim and quit the editor is :wq.
To save the file and exit the editor simultaneously, press Esc to switch to normal mode, type :wq and hit Enter.

- Press
Esc - Type
:wq - Press
Enter
Another command to save a file and quit Vim is :x.
The difference between these two commands is that :x writes the buffer to the file only if there are unsaved changes, whereas :wq always writes the buffer to file and updates the file modification time.
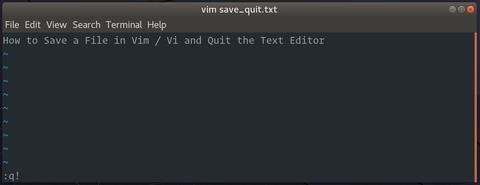
Quit Vim / Vi without Saving the File
To exit the editor, without saving the changes, switch to normal mode by pressing Esc, type :q! and hit Enter.
- Press
Esc - Type
:q! - Press
Enter
Conclusion
In this guide, we have shown you how to save a file in Vim and exit the editor. If you are new to Vim, visit the Open Vim site where you can practice Vim with an interactive tutorial.
Feel free to leave a comment if you have any questions.
VIM Editor Commands
Vim is an editor to create or edit a text file.
There are two modes in vim. One is the command mode and another is the insert mode.
In the command mode, user can move around the file, delete text, etc.
In the insert mode, user can insert text.
Changing mode from one to another
From command mode to insert mode type a/A/i/I/o/O ( see details below)
From insert mode to command mode type Esc (escape key)
Some useful commands for VIM
Text Entry Commands (Used to start text entry)
a Append text following current cursor position
A Append text to the end of current line
i Insert text before the current cursor position
I Insert text at the beginning of the cursor line
o Open up a new line following the current line and add text there
O Open up a new line in front of the current line and add text there
The following commands are used only in the commands mode.
Cursor Movement Commands
h Moves the cursor one character to the left
l Moves the cursor one character to the right
k Moves the cursor up one line
j Moves the cursor down one line
nG or :n Cursor goes to the specified (n) line
(ex. 10G goes to line 10)
^F (CTRl F) Forward screenful
^B Backward screenful
^f One page forward
^b One page backward
^U Up half screenful
^D Down half screenful
$ Move cursor to the end of current line
0 (zero) Move cursor to the beginning of current line
w Forward one word
b Backward one word
Exit Commands
:wq Write file to disk and quit the editor
:q! Quit (no warning)
:q Quit (a warning is printed if a modified file has not been saved)
ZZ Save workspace and quit the editor (same as :wq)
: 10,25 w temp
write lines 10 through 25 into file named temp. Of course, other line
numbers can be used. (Use :f to find out the line numbers you want.
Text Deletion Commands
x Delete character
dw Delete word from cursor on
db Delete word backward
dd Delete line
d$ Delete to end of line
d^ (d caret, not CTRL d) Delete to beginning of line
Yank (has most of the options of delete)– VI’s copy commmand
yy yank current line
y$ yank to end of current line from cursor
yw yank from cursor to end of current word
5yy yank, for example, 5 lines
Paste (used after delete or yank to recover lines.)
p paste below cursor
P paste above cursor
“2p paste from buffer 2 (there are 9)
u Undo last change
U Restore line
J Join next line down to the end of the current line
File Manipulation Commands
:w Write workspace to original file
:w file Write workspace to named file
:e file Start editing a new file
:r file Read contents of a file to the workspace
To create a page break, while in the insert mode, press the CTRL key
And l. ^L will appear in your text and will cause the printer to start
A new page.
Other Useful Commands
Most commands can be repeated n times by typing a number, n, before
the command. For example 10dd means delete 10 lines.
. Repeat last command
cw Change current word to a new word
r Replace one character at the cursor position
R Begin overstrike or replace mode � use ESC key to exit
:/ pattern Search forward for the pattern
😕 pattern Search backward for the pattern
n (used after either of the 2 search commands above to
continue to find next occurrence of the pattern.
:g/pat1/s//pat2/g replace every occurrence of pattern1 (pat1) with
pat2
Example :g/tIO/s//Ada.Text_IO/g
This will find and replace tIO by Ada.text_IO everywhere in the file.
:g/a/s// /g replace the letter a, by blank
:g/a/s///g replace a by nothing
note: Even this command be undone by u
Examples
Opening a New File
Step 1 type vim filename (create a file named filename)
Step 2 type i ( switch to insert mode)
Step 3 enter text (enter your Ada program)
Step 4 hit Esc key (switch back to command mode)
Step 5 type :wq (write file and exit vim)
Editing the Existing File
Step 1 type vim filename (edit the existing file named filename)
Step 2 move around the file using h/j/k/l key or any appropriate command
h Moves the cursor one character to the left
l Moves the cursor one character to the right
k Moves the cursor up one line
j Moves the cursor down one line
nG or :n Cursor goes to the specified (n) line
(ex. 10G goes to line 10)
Step 3 edit required text (replace or delete or insert)
Step 4 hit Esc key (exit from insert mode if you insert or replace text)
Step 5 type :wq


