+ KLWP INFO
https://www.jagwar.de/kustom-beginners-guide-part-1-klwp-basics/
After introducing Kustom and posting some Tutorials I noticed the lack of a real Beginner's Guide to Kustom and the first steps are quite irritating coming from Zooper. This Kustom Beginner's Guide should give an overview of KLWP Basics with new parts coming for more detailed help.
Kustom Live Wallpaper, created by "Kustom Industries," is a live wallpaper tool that allows you to create your theme directly in the live wallpaper itself. This allows fluid transitions in widgets and a host of other things that would have otherwise been impossible due to launcher limitations. (via reddit androidhemes wiki)
Kustom Beginner's Guide – Part 1 – KLWP Basics
I'm pretty sure that Kustom will become the most popular app to create a totally unique and efficient designs for your android homescreen. There are many users in communities and on reddit showing how elegant and interactive the designs can be. With these basics it should be easy for you to produce some nice designs.
Getting Started
If you don't have Kustom already installed, get it from the Play Store. You can start this Kustom Beginner's Guide with the free version but I would recommend to go Pro InApp or with this Key because it will give you extra features that come in handy.
– Remove the ADS
– Unlock import from SD and all external skins
– Allow exporting skins to SD and creation of APK preset packs
Crucial here is the import and export function because its often easy to learn by studying other walls or komponents.
Organization
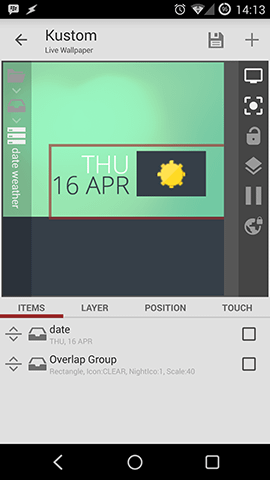
The first thing to understand is that you don't need to add a widget which you later edit in the app. In Kustom you design a whole wallpaper and set it as background. This wallpaper can contain so called komponents which can be shared separately, so you don't need to share your whole design. Komponents could be called widgets and can be a clock, weather icons or almost anything else.
Interface
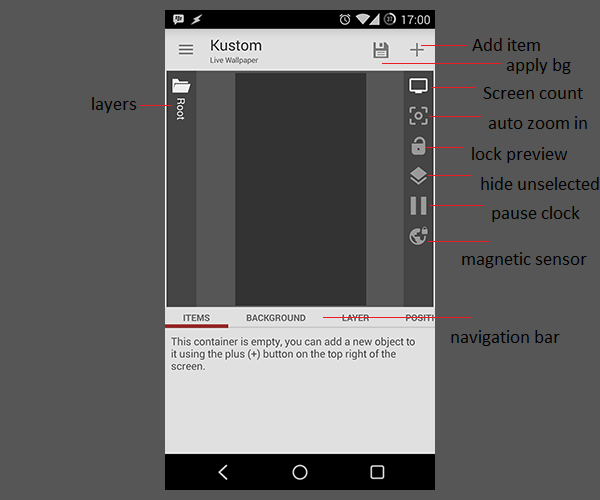
Kustoms comes with an easy to use interface. Most of the specific functions of the interface I'll cover in future parts of the Kustom Beginner's Guide, for now you can acquaint yourself with the layers menu on the left side. After adding new items to your preset you can navigate easily through the layer menu. On the right side you have the add new items button and some options to make designing presets easier. You can automatically zoom into smaller parts of you screen or pause clock animations. On the bottom you have the navigation bar with all options to adjust your items. The bar changes depending on your current item.
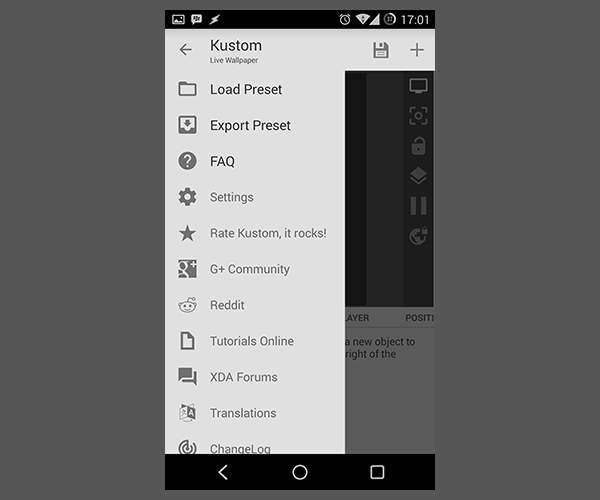
The hamburger menu on the left side contains load and export functions for your whole wallpaper, setting and some links. Make sure to check the FAQ and rate Kustom!
Settings
One of the first things to do is to adjust the settings your way. I would advise you to change your app language to English since all the tutorials published on every site will be in English and it will be way easier to work with the Kustom Beginner's Guide that way.
Load Preset
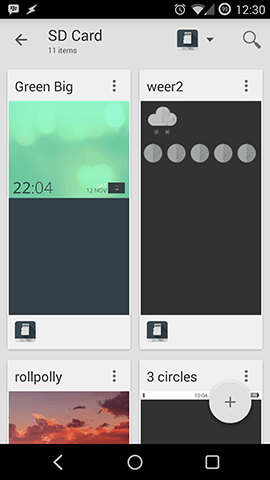
To load a preset open the menu and pick Load Preset. You will be presented with some preloaded presets and can pick one to open (my screenshot just shows the presets on my SD Card). To make a new preset or import one press the add button and you will see a menu.
Add items
A preset or wall consists of items, to add one just press the "+" on the top right. I think text, shape, image and progress bars are self explaining.
Komponent
Komponents are intended to make sharing parts of walls easier. You could think of it as a widget and it's possible to put all the other items into it. You don't have to start with a komponent, you can copy all your items into one after you are finished with the design, more to that in the clean design art of this Kustom Beginner's Guide.
Komponents are also the only way for weather iconsets inside Kustom. the difference to Zooper is that here you have to add a weather komponent and not the iconset directly.
The "Komponent" is a special Overlap Layer that can be exported and reused. The "Komponent" group is like a preset within a preset and allows you to create your own modules with their own global variables. So, for example, if you create a Clock you can then export the Komponent and add this clock to other presets by loading it in one shot, the globals of the Komponent will become the settings of it so when using the module you will not see the objects inside (unless you unlock it) but just the basic settings. Komponents can also be distributed via APK. Please check the tutorials section for more examples. (via kustom.uservoice.com)
There will be a special, more detailed post for komponents in the Kustom Beginner's Guide.
Overlap Group
Overlap groups are the easiest way to arrange items over each other. Only now you can use drawing modes (not possible with items in the root layer).
The "Overlap" group is a container for other modules, the layer size will increase based on its contents so it will basically "wrap" the items inside it. As the name suggest the "Overlap" group will place the items one on top of the other, you will then need to use the padding or the anchor to move them inside, the anchor is relative to the Group so if you anchor something "top left" in an Overlap Group it will be the top left of the group itself.
Benefits of using an Overlap Group are:
- You can scale all items inside the group together by using the Layer -> Scale property
- On a Wallpaper root you can "repeat" or "mirror" the layer using the "Tiling" option, this is very useful in order to create pattern based wallpapers
- You can animate, move and re position all items together
- Overlap Group provides "static center" rotation, so, if you enable rotation of a group the group will rotate based on the group center, so the overlap group is the basis to create clock hands (see the clock tutorial in the tutorials section)
(via kustom.uservoice.com)
There will be a more detailed post for overlay and stack groups in the Kustom Beginner's Guide.
Stack Group
This item comes in really handy. In other customization apps you always had to position items manually and rearrange them when sizes changed. With Stack Groups you can easily arrange items horizontally or vertically.
For example here you can see a stack group and an overlap group inside a stack group. The big stack group stacks two items (Day/Date stack and Weather overlay) horizontally, the Day/Date stack group stacks to text items vertically together and the overlap group is a background and the weather komponent.
With this groups it's really easy to change sizes or move the thing altogether.
A stack group is a container that allows automatic "stacking" of the items, so if you want to have multiple text items placed one after the other horizontally or vertically you will use a Stack. This is especially good when you want to place one item just after another but the item size might change dynamically. The stack allows also to anchor items all to one side of the group, try playing with the stacking option in the "Layer" section. (via kustom.uservoice.com)
There will be a more detailed post for overlay and stack groups in the Kustom Beginner's Guide.
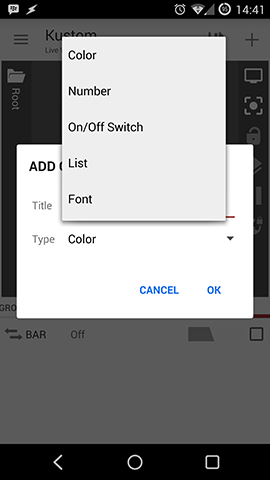
Globals
Global variables are there to make bulk changes to items easier. For example, it's quite easy to change the color of all items with one global variable.
Globals can be:
- Color
- Number
- On/Off Switch
- List
- Font
If you open the Advanced Editor you will notice on the first "root" container a tab called "globals", that section will allow you to add / remove and change Global variables which are just settings that can be applied to multiple modules at once. So, how to use them?
So let's say you have a preset with a lot of text items around and you decide that you want to change the font of all of these very quickly from a single setting point, so, in this case, you use a Global, so you:
- Create a Global of type "Font" in the Globals section mentioned above
- You go in the TextModule, select the "Font" preference and then click on the "Globe" icon in the actionbar on top
- Then you click again on the option and select the Global you just created from the list
- Repeat this for all the Text modules you want to change with that global
That's it! You can now change the font of all these modules just changing the Global preference in the main container.
(via kustom.uservoice.com)
There will be a more detailed post for globals in the Kustom Beginner's Guide.
Animations
One of the big advantages of Kustom are animations. With this you can create interactive design with almost no limits.
In Kustom all items placed in the "root" module can be animated, in order to do so please use the "animation" tab and add one or more animations. If more than one animation is added the animations will be combined, the order is not relevant.
Animations have a lot of parameters, let's see what they do:
- ReactOn this will control when the animation will be triggered, currently only "scroll" is supported which means that it will be activated by screen swiping
- Action represents the type of animation to perform, scroll and scroll inverted will move the object horizontally, fade will change its transparency, scale will change the size and rotate will rotate the object
- Center decides in which screen the item will be in its "starting" position so this is where the animation will start from, for example, if you have a centered item and center set to screen 1 the item will be centered on screen 1 and start moving from there
- Speed controls how fast the "action" is performed, for example when fading at speed 100 in scroll the item will go from full opacity to fully transparent in one screen, if speed is 50 it will take 2 screens to fade out
- Amount will decide when to stop, 100 means that the full animation will be applied (so, in case of fade it will go from full opacity to transparent), 50 means that only 50% will be applied, so when opacity will be 50% it will stop. This is available only on certain animations.
- Rule controls when this animation is applied, so for example "before center" will tell the animator to use the animation only up to the center and ignore it after it. The default is "center" which means that animation will be applied before and after the center.
- Anchor will set the anchor point for a rotation or a scaling
(via kustom.uservoice.com)
There will be a more detailed post for animations in the Kustom Beginner's Guide.
Kustom Beginner's Guide – Part 1 – KLWP Basics
This part of the Kustom Beginner's Guide should have given you a basic overview of the functionalities and you can start to build your own simple walls and komponents. I will continue with some more detailed guides.
More information on Kustom is available here.
KLWP Live Wallpaper Maker (Playboard) | KLWP Live Wallpaper Maker (Play Store)
KLWP Live Wallpaper Pro Key (Playboard) | KLWP Live Wallpaper Pro Key (Play Store)
https://dribbble.com/tags/klwp?page=2 (some klwp examples)
https://www.jagwar.de/klwp-functions/
Since the KLWP Functions are on many different pages on the original Kustom webpage I made easy searchable tables on one side to go along nicely with my Formulas, Funtions and Kodes guide.
KLWP Functions
This is nothing new, all credits go to +Frank Monza!
DF: Format a Date into text
Syntax: df(format, [date])
Arguments
- format: Format to be used for the date, see examples
- date: Date to be used. The Date can be returned by some other function or you can use text. For text dates you can both set it statically using the format '1955y11M12d22h04m00s' to express year 1955, month 11, day 12 at 22:04:00 (all fields are optional), or use 'a/r' (add/remove) operators, so, for example 'a12m3s' will add 12 minutes and 3 secs to current date.
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| df(format, [date]) | $df(h:mm)$ | Hours and minutes with padding zero |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(hh:mma)$ | Hours with leading zero, minutes and AM/PM marker (if 12h format in use) |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(hh:mm:ssa)$ | Hours with leading zero, minutes, seconds and AM/PM marker (if 12h format in use) |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(d MMM yyyy)$ | Current day number, month short name and full year |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(dd/MM/yyyy)$ | Day / Month / Year numbers |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(hh)$ | Hours with padding zero |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(mm)$ | Minutes with padding zero |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(ss)$ | Seconds with padding zero |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(dd)$ | Day of the month with padding zero |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(EEEE)$ | Current day name |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(EEE, a1d)$ | Tomorrow's short day name |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(MMMM)$ | Current month name |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(D)$ | Day of year (number) |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(w)$ | Week of year |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(e)$ | Current day of the week (number) |
| df(format, [date]) | $df(f)$ | ISO day of week (number, 1=Monday) |
TF: Format a time span (es "3 hours ago")
Syntax: tf(date, [format])
Arguments
- date: Date to be used. The Date can be returned by some other function or you can use text. For text dates you can both set it statically using the format '1955y11M12d22h04m00s' to express year 1955, month 11, day 12 at 22:04:00 (all fields are optional), or use 'a/r' (add/remove) operators, so, for example 'a12m3s' will add 12 minutes and 3 secs to current date.
- format: Optional format to be used for the time, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tf(date, [format]) | $tf(bi(plugged))$ | Time since last battery plugged/unplugged |
| tf(date, [format]) | Midnight $tf(0h0m0sa1d)$ | Time to midnight (we first set the time to 0 hours, 0 mins and 0 sec then we add one day at the end) |
| tf(date, [format]) | Midnight in $tf(0h0m0sa1d, hh:mm:ss)$ | Countdown to midnight (same as before but we use custom format) |
| tf(date, [format]) | $tf(ai(sunset) – ai(sunrise))$ | Current duration of daylight, automatic format |
| tf(date, [format]) | Tonight $tf(ai(sunrise, a1d) – ai(sunset), "h' hours' and m' minutes'")$ of darkness | Darkness duration, manual format |
| tf(date, [format]) | Sunrise in $tf(ai(nsunrise), M)$ minutes | Minutes till next sunrise |
LI: Location info (latitude, longitude, address)
Syntax: li(type)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| li(type) | $li(loc)$ | Current Locality (ex "Hill Valley", if available) |
| li(type) | $li(country)$ | Current Country Name (ex "Iceland", if available) |
| li(type) | $li(ccode)$ | Current Country Code (ex US, if available) |
| li(type) | $li(addr)$ | Current Address (if available) |
| li(type) | $li(admin)$ | Current Admin Area (ex CA, if available) |
| li(type) | $li(postal)$ | Current Postal Code (if available) |
| li(type) | $li(spd)$ | Current Speed in local unit (kmh/mph if available, 0 otherwise) |
| li(type) | $li(spdm)$ | Current Speed in meters per second (if available, 0 otherwise) |
| li(type) | $li(spdu)$ | Current Speed unit (kmh/mph) |
| li(type) | $li(alt)$ | Altitude in local unit (meters/feet with GPS lock only, 0 otherwise) |
| li(type) | $li(altm)$ | Altitude in meters (with GPS lock only, o otherwise) |
| li(type) | $li(lat)$ | Latitude |
| li(type) | $li(lon)$ | Longitude |
| li(type) | $li(lplat)$ | Latitude (low precision ~50m) |
| li(type) | $li(lplon)$ | Longitude (low precision ~50m) |
WI: Weather info (temperature, conditions)
Syntax: wi(type)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wi(type) | $wi(temp)$$wi(tempu)$ | Temperature in local unit |
| wi(type) | $wi(flik)$$wi(tempu)$ | Feels Like temperature (Heat Index) in local unit |
| wi(type) | $wi(cond)$ | Current weather condition |
| wi(type) | $df("hh:mma", wi(updated))$ | Time of last weather update in hh:mm format |
| wi(type) | $wi(provider)$ | Weather provider used to fetch data |
| wi(type) | $wi(icon)$ | Current weather icon, one of: UNKNOWN, TORNADO, TSTORM, TSHOWER, SHOWER, RAIN, SLEET, LSNOW, SNOW, HAIL, FOG, WINDY, PCLOUDY, MCLOUDY, CLEAR |
| wi(type) | $wi(code)$ | Current weather code, one of: TORNADO, TROPICAL_STORM, HURRICANE, SEVERE_THUNDERSTORMS, THUNDERSTORMS, MIXED_RAIN_SNOW, MIXED_RAIN_SLEET, MIXED_SNOW_SLEET, FREEZING_DRIZZLE, DRIZZLE, FREEZING_RAIN, SHOWERS, HEAVY_SHOWERS, SNOW_FLURRIES, LIGHT_SNOW_SHOWERS, BLOWING_SNOW, SNOW, HAIL, SLEET, DUST, FOGGY, HAZE, SMOKY, BLUSTERY, WINDY, CLOUDY, MOSTLY_CLOUDY, PARTLY_CLOUDY, CLEAR, FAIR, MIXED_RAIN_AND_HAIL, ISOLATED_THUNDERSTORMS, SCATTERED_SHOWERS, HEAVY_SNOW, SCATTERED_SNOW_SHOWERS, THUNDERSHOWERS, SNOW_SHOWERS, ISOLATED_THUNDERSHOWERS, NOT_AVAILABLE |
| wi(type) | $wi(wspeed)$$li(spdu)$ | Wind Speed in local unit (kmh/mph) |
| wi(type) | $wi(wspeedm)$mps | Wind Speed in meters per second |
| wi(type) | $wi(wchill)$$tc(utf, b0)$$wi(tempu)$ | Wind Chill in local unit |
| wi(type) | $wi(wdir)$ | Wind Direction in degrees |
| wi(type) | $wi(press)$mbar | Current pressure in Millibars |
| wi(type) | $wi(hum)$% | Current humidity in percent |
WF: Weather forecast info (max/min temperature, conditions)
Syntax: wf(type, day)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
- day: Forecast day index (0 is today)
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wf(type, day) | $wf(min, 0)$$wi(tempu)$ | Today's min temperature in local unit |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(max, 0)$$wi(tempu)$ | Today's max temperature in local unit |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(cond, 0)$ | Today's forecast condition |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(icon, 0)$ | Today's forecast icon, one of: UNKNOWN, TORNADO, TSTORM, TSHOWER, SHOWER, RAIN, SLEET, LSNOW, SNOW, HAIL, FOG, WINDY, PCLOUDY, MCLOUDY, CLEAR |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(code, 0)$ | Today's forecast code, one of: TORNADO, TROPICAL_STORM, HURRICANE, SEVERE_THUNDERSTORMS, THUNDERSTORMS, MIXED_RAIN_SNOW, MIXED_RAIN_SLEET, MIXED_SNOW_SLEET, FREEZING_DRIZZLE, DRIZZLE, FREEZING_RAIN, SHOWERS, HEAVY_SHOWERS, SNOW_FLURRIES, LIGHT_SNOW_SHOWERS, BLOWING_SNOW, SNOW, HAIL, SLEET, DUST, FOGGY, HAZE, SMOKY, BLUSTERY, WINDY, CLOUDY, MOSTLY_CLOUDY, PARTLY_CLOUDY, CLEAR, FAIR, MIXED_RAIN_AND_HAIL, ISOLATED_THUNDERSTORMS, SCATTERED_SHOWERS, HEAVY_SNOW, SCATTERED_SNOW_SHOWERS, THUNDERSHOWERS, SNOW_SHOWERS, ISOLATED_THUNDERSHOWERS, NOT_AVAILABLE |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(wspeed, 0)$$li(spdu)$ | Wind Speed in local unit (kmh/mph) |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(wspeedm, 0)$mps | Wind Speed in meters per second |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(wdir, 0)$ | Wind Direction in degrees |
| wf(type, day) | $wf(hum, 0)$% | Current humidity in percent |
NC: Network Connectivity (wifi / phone signal, operator name, network state)
Syntax: nc(text)
Arguments
- text: Info type, see examples and reference
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| nc(text) | $nc(csig)$ | Cell signal from 0 to 4 |
| nc(text) | $nc(operator)$ | Current cell operator |
| nc(text) | $nc(dtype)$ | Current cellular data connection type (LTE, HSUPA) |
| nc(text) | $nc(dtypes)$ | Current cellular data connection short type (4G, 3G) |
| nc(text) | $nc(ssid)$ | Current WiFi SSID (if connected) |
| nc(text) | $nc(wsig)$ | Wifi signal from 0 to 9 |
| nc(text) | $nc(csiga)$ | Cell signal level as an asu value between 0..31, 99 is unknown |
| nc(text) | $nc(csigd)$ | Cell signal level in dbm |
| nc(text) | $nc(wrssi)$ | Wifi signal raw (RSSI) |
| nc(text) | $nc(wspeed)$ | Wifi speed in Megabit |
| nc(text) | $nc(bt)$ | Current BlueTooth static, 0 disabled, 1 enabled |
| nc(text) | $nc(cell)$ | Current cellular status, one of:: OFF, AIRPLANE, ON, DATA, ROAMING, DATAROAMING |
| nc(text) | $nc(wifi)$ | Current WiFi status, one of:: DISABLED, ENABLED, CONNECTED |
BI: Battery info (level, voltage, temperature, time since charging)
Syntax: bi(type, [date])
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
- date: Optional date for historical data up to 24 hours, you can use usual format so, "r1h" will give one hour ago, "r30m" 30 minutes ago and so on (see examples)
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(level)$% | Battery Level (in %) |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(temp)$$wi(tempu)$ | Battery Temperature in local unit |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(tempc)$ | Battery Temperature in celsius |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(volt)$ | Battery voltage in millivolts |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(charging)$ | Will return 0 if on Battery, 1 if charging from AC, 2 for USB and 4 for Wireless |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(source)$ | Current power source (Battery, AC, USB or Wireless) |
| bi(type, [date]) | $df("hh:mma", bi(plugged))$ | Date of last plugged / unplugged event |
| bi(type, [date]) | $if(bi(charging) = 0, "unplugged", "plugged")$ $tf(bi(plugged))$ | Time since last plugged / unplugged event |
| bi(type, [date]) | $df("hh:mma", bi(fullempty))$ | Date of expected next charged/discharged event |
| bi(type, [date]) | $if(bi(charging) = 0, discharged, charged)$ $tf(bi(fullempty))$ | Time to next expected charged/discharged event |
| bi(type, [date]) | $if(bi(charging) = 0, Discharged, Full)$$if(bi(charging) = 0 | bi(level) < 100, " in " + tf(bi(fullempty) – dp()))$ | Alternate time to next expected charged/discharged event with relative time |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(level, r30m)$% | Battery Level (in %) 30 minutes ago |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(source, r1h)$ | Battery Source 1 hour ago |
| bi(type, [date]) | $bi(temp, r2h)$$wi(tempu)$ | Battery Temp 2 hours ago |
SI: System info (next alarm, uptime, model, rom)
Syntax: si(type)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| si(type) | $df("EEE hh:mma", si(alarmd))$ | Next alarm formatted date (if set) |
| si(type) | $si(alarmt)$ | Next alarm as original text |
| si(type) | $si(alarmon)$ | Alarm switch, return 1 if alarm is set, 0 otherwise |
| si(type) | Next alarm $tf(si(alarmd))$ | Time to next alarm (if set) |
| si(type) | $si(land)$ | Screen Orientation (gives 0 in portrait, 1 if landscape) |
| si(type) | $si(locked)$ | Device Lock (gives 1 if locked, 0 if not) |
| si(type) | Uptime: $tf(df(S) – df(S, si(boot)))$ | Time since boot (uptime) |
| si(type) | $si(screen)$ | Current desktop screen (if supported) |
| si(type) | $si(screenc)$ | Current desktop screen count (if supported) |
| si(type) | $si(model)$ | Phone Model |
| si(type) | $si(man)$ | Phone Manufacturer |
| si(type) | $si(build)$ | ROM Name |
RM: Resource Monitor (cpu, memory)
Syntax: rm(type, [fs])
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
- fs: FS to get stats from, use "int" for internal, "ext" for SD (default) or specify custom absolute path
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(cidle)$% | Current idle cpu in % |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(cused)$% | Current used (sys + usr) cpu in % |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(cusr)$% | Current user cpu in % |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(csys)$% | Current system cpu in % |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fmin)$Mhz | Min CPU frequency in Mhz |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fmax)$Mhz | Max CPU frequency in Mhz |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fcur)$Mhz | Current CPU frequency in Mhz |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(mtot)$MB | Total memory in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(mfree)$MB | Free memory in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(mused)$MB | Used memory in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fstot)$MB | Total SD FS space in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fsfree)$MB | Free SD FS space in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fsused)$MB | Used SD FS space in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fstot, int)$MB | Total internal FS space in Mb |
| rm(type, [fs]) | $rm(fsfree, int)$MB | Free internal FS space in Mb |
AI: Astronomical info (sunrise, suset, isday)
Syntax: ai(type)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ai(type) | $df("hh:mma", ai(sunrise))$ | Today's sunrise in hh:mm format |
| ai(type) | $df("hh:mma", ai(sunset))$ | Today's sunset in hh:mm format |
| ai(type) | $ai(isday)$ | Will return 1 during daylight or 0 if night |
| ai(type) | $tf(ai(nsunrise))$ | Time to next sunrise |
| ai(type) | $tf(ai(nsunset))$ | Time to next sunset |
CI: Calendar events
Syntax: ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar])
Arguments
- action: Action (see examples)
- index: Index of upcoming events if no date is provided, index of day events if date is added. When prefixed with an "a" will show only all day events, with "e" only normal ones. Index is zero based, 0 is the first event, 1 the second and so on, a0 is the first all day event, e0 the first non all day one.
- date: Date to be used. The Date can be returned by some other function or you can use text. For text dates you can both set it statically using the format '1955y11M12d22h04m00s' to express year 1955, month 11, day 12 at 22:04:00 (all fields are optional), or use 'a/r' (add/remove) operators, so, for example 'a12m3s' will add 12 minutes and 3 secs to current date.
- calendar: Override default Calendar selection
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $df(EEE hh:mm, ci(start, 0))$-$df(hh:mm, ci(end, 0))$ $ci(title, 0)$ | Day start-end title of first upcoming event |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(title, 1)$ | Title of second upcoming event |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(desc, 1)$ | Description of second upcoming event or all day event (the first) |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $df("hh:mma", ci(start, 0))$ | Start date of next upcoming event in HH:MM format |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(allday, 0)$ | Will write 1 if next upcoming event is allday, 0 otherwise |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(title, a0, a0d)$ | Title of today's first all day event |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(desc, e1, a0d)$ | Description of today's second event |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(ccolor, e1, a1d)$ | Calendar Color of first event tomorrow |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(cname, a1, a1d)$ | Calendar Name of first all day event tomorrow |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $df("hh:mma", ci(end, 0, a0d))$ | End date of second event today in HH:MM format |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(color, 1, a1d)$ | Color of second event tomorrow |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(ecount, a0d)$ | Number of appointments today |
| ci(action, [index], [date], [calendar]) | $ci(acount, a1d)$ | Number of all day events tomorrow |
MI: Music Info (playing track, artist)
Syntax: mi(type)
Arguments
- type: Info type, see examples
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mi(type) | $mi(album)$ | Current Album (if set) |
| mi(type) | $mi(artist)$ | Current Artist (if set) |
| mi(type) | $mi(title)$ | Current Track Title (if set) |
| mi(type) | $tf(mi(len), mm:ss)$ | Current Track Duration (in mm:ss format) |
| mi(type) | $tf(mi(pos), mm:ss)$ | Current Track Position (in mm:ss format) |
| mi(type) | $mi(len)$ | Current Track Duration (in seconds) |
| mi(type) | $mi(pos)$ | Current Track Position (in seconds) |
| mi(type) | $mi(percent)$ | Current Track Position (in percentage) |
| mi(type) | $mi(cover)$ | Current Cover Image (to be used in Image module or Background as formula) |
| mi(type) | $mi(package)$ | Current Player Package Name |
| mi(type) | $mi(state)$ | Current Player State, one of:: STOPPED, PAUSED, PLAYING, FORWARDING, REWINDING, SKIPPING_FORWARDS, SKIPPING_BACKWARDS, BUFFERING, ERROR, NONE |
TC: Text converter (lowercase, uppercase, capitalized, regexp)
Syntax: tc(mode, text)
Arguments
- mode: Conversion mode, "l" for lowercase, "u" for uppercase, "c" for capitalize
- text: Text to convert
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(low, "sOme tExT")$ | Convert text to lower case |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(up, "sOme tExT")$ | Convert text to upper case |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(cap, "sOme tExT")$ | Capitalize words in text |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(cut, "sOme tExT", 4)$ | Will print only first 4 chars |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(ell, "sOme tExT", 4)$ | Will ellipsize (so cut and add "") if text is longer than 4 chars |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(utf, "201")$ | Will render utf code 0x201 (advanced, for font icons) |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(len, "sOme tExT")$ | Will return the length of text |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(ord, 1)$ | Renders ordinal suffix for number 1 (st) |
| tc(mode, text) | $tc(reg, "Foobar one", "o+", X)$ | Will replace text matching "o+" regexp with a capital X |
IF: If conditions (if/then/else support with multiple boolean operators)
Syntax: if(condition, then, [else])
Arguments
- condition: A condition can use any comparison like "=" (equals), ">" (greater), ">=" (greater or equal), "<" (less), "<=" (less or equal) combined with boolean operators "&" (AND) or "|" (OR) and parenthesis
- then: Text or function to use if condition is true (so if return value is not empty and not "0")
- else: Optional text or function to be called if condition is false (so either empty or "0")
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| if(condition, then, [else]) | Battery $if(bi(level) = 100, "is Fully Charged", if(bi(level) <=15, "is Critically Low", "is at " + bi(level) + "%" ))$ | Shows status of battery writing "fully charged" when full, "critical" if below 15 or the normal level otherwise | |||
| if(condition, then, [else]) | $if(df(f)>5, "Week End!", "Workday :(")$ | Will show "Week End!" during week ends or "Workday :(" during workdays |
WG: WGet, retrieve text, rss and other content from HTTP links
Syntax: wg([url], filter, params)
Arguments
- url: Url to the http content
- filter: Filter to use (currently only RSS and TXT are supported)
- params: Filter parameters (see examples)
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("goo.gl/vtJASB")$ | Write quote of the day URL content without parsing |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("goo.gl/wNMV3f", txt)$ | Convert HTML content at URL into plain Text |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("api.theysaidso.com/qod.xml", xml, "response/contents/quote")$ | Parse XPath expression for XML content at URL |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("http://www.cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, title)$ | Get RSS feed title |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, desc)$ | Get RSS feed description |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $df("hh:mma", wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, date))$ | Get RSS feed publish date |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, count)$ | Get RSS feed entry count |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, 0, title)$ | Get RSS feed title for entry 0 |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, 0, desc)$ | Get RSS feed content for entry 0 |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, 0, link)$ | Get RSS feed link for entry 0 |
| wg([url], filter, params) | $wg("cnet.com/rss/news/", rss, 0, thumb)$ | Get RSS feed first thumbnail image for entry 0 |
TS: Traffic Stats (download / upload speed)
Syntax: ts(type, [unit])
Arguments
- type: Data type (use "trx" for total bytes download and "ttx" for total uploaded)
- unit: Unit, a for "auto" (default, will add unit), b for bytes, k for kilobytes or m for megabytes
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ts(type, [unit]) | $ts(trx)$ | Current download speed in automatic unit |
| ts(type, [unit]) | $ts(ttx)$ | Current download speed in automatic unit |
MU: Math Utilities (floor, ceil, sqrt, min, max)
Syntax: mu(var, [default])
Arguments
- var: Function (one of ceil, floor or sqrt)
- default: One or more values depending on the function
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(ceil, 3.14)$ | Will return ceil of 3.14 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(floor, 3.80)$ | Will return floor of 3.80 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(sqrt, 2)$ | Will return square root of 2 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(round, 2.80)$ | Will round 2.80 to the nearest integer |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(min, 1, 3)$ | Will return min between 1 and 3 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(max, 1, 3)$ | Will return max between 1 and 3 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(abs, -1)$ | Will return absolute value of -1 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(cos, 90)$ | Cosine of 90 degrees |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(sin, 90)$ | Sine of 90 degrees |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(tan, 45)$ | Tangent of 45 degrees |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(atan, 45)$ | Inverse Tangent of 45 degrees |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(log, 5)$ | Logarithm of 5 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(ln, 5)$ | Natural logarithm of 5 |
| mu(var, [default]) | $mu(rnd, 10, 100)$ | Random number between 10 and 100 |
CM: Color Maker, generate colors from ARGB/AHSV values
Syntax: cm([a], r/h, g/s, b/v, [mode])
Arguments
- a: Alpha value (optional, 0 is transparent 255 is fully opaque, default 255)
- r/h: Red (0-255) / Hue (0-360)
- g/s: Green (0-255) / Saturation (0-100)
- b/v: Blue (0-255) / Value (0-100)
- mode: Color mode (r for ARGB, h for AHSV, optional, default is ARGB)
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cm([a], r/h, g/s, b/v, [mode]) | $cm(128,255,0,0)$ | Will generate a 50% transparent red color #FFFF0000 |
| cm([a], r/h, g/s, b/v, [mode]) | $cm(0,df(ss)4.25,255-df(ss)4.25)$ | Will move from blue to green based on seconds |
CE: Color Editor to manipulates ARGB color values
Syntax: ce(color, filter, amount)
Arguments
- color: A valid ARGB or RGB color String (es #FF663399)
- filter: Filter ("alpha" opacity, "sat" saturation, "lum" luminance)
- amount: A value between 0 and 100, for alpha 0 is fully transparent, for saturation 0 means greyscale and for luminance 0 is black
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ce(color, filter, amount) | $ce(#FF0000, alpha, 50)$ | Will make a fully opaque red into 50% transparent |
| ce(color, filter, amount) | $ce(#FF0000, sat, 0)$ | Will convert red color into Greyscale equivalent |
| ce(color, filter, amount) | $ce(#FF0000, lum, 50)$ | Will set red luminance to 50 |
| ce(color, filter, amount) | $ce(#FF0000, lum, a50)$ | Will add 50 to red luminance (0 to 100) |
| ce(color, filter, amount) | $ce(#FF0000, alpha, r50)$ | Will remove 50 from red alpha (0 to 255) |
GV: Global Variables (will return the value of a global variable)
Syntax: gv(var, [default])
Arguments
- var: The key of the global to retrieve
- default: An optional default to return if global is not found
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| gv(var, [default]) | $gv(fgcolor, #FF0000)$ | Will return the value of var "fgcolor" or red color if not found |
DP: Creates a date from text
Syntax: dp(date)
Arguments
- date: Date to be used. The Date can be returned by some other function or you can use text. For text dates you can both set it statically using the format '1955y11M12d22h04m00s' to express year 1955, month 11, day 12 at 22:04:00 (all fields are optional), or use 'a/r' (add/remove) operators, so, for example 'a12m3s' will add 12 minutes and 3 secs to current date.
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dp(date) | $dp(0h0m0s)$ | Today's midnight |
| dp(date) | $dp(01m01d0h0m0sa1y)$ | New year's eve |
BR: Broadcast Receiver (get variables from third parties, es Tasker)
Syntax: br(source, var)
Arguments
- source: Source name, es "tasker" or "zooper"
- var: Variable name, if the variable contains a formula the formula will be parsed
Search:
| Syntax | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| br(source, var) | $br(tasker, FOOBAR)$ | Will write the value of variable FOOBAR sent from Tasker action plugin |
| br(source, var) | $br(zooper, FOOBAR)$ | Will write the value of variable FOOBAR sent to Zooper from Tasker or third party plugins (equivalent in Zooper would be #TFOOBAR#) |